Cultural Heritage at Risk: Rapid Diminishing of World’s Built Heritage

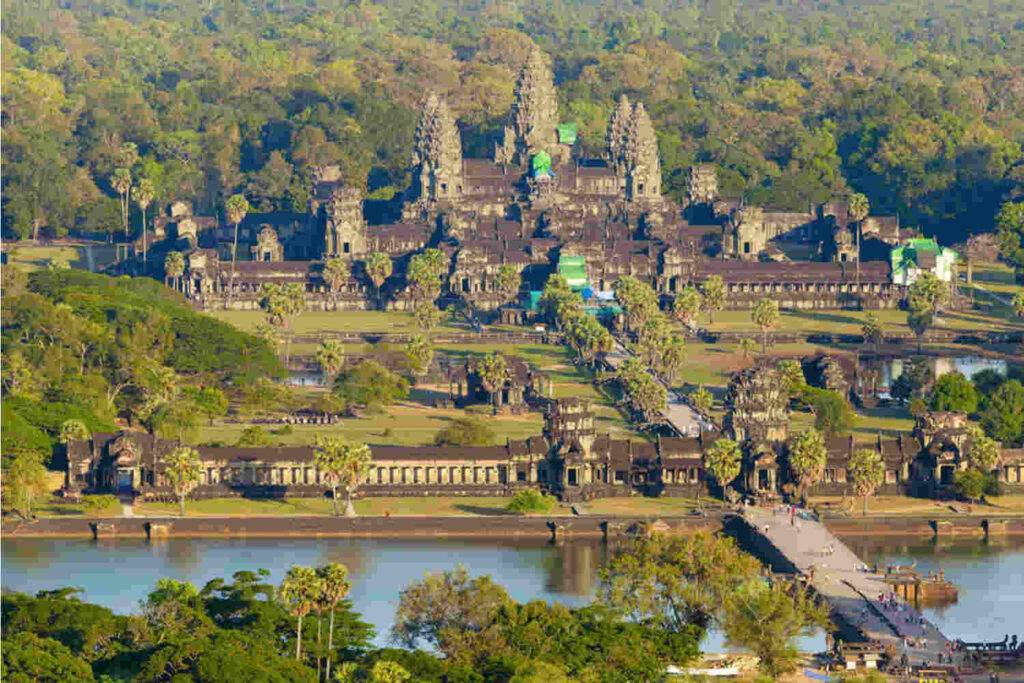
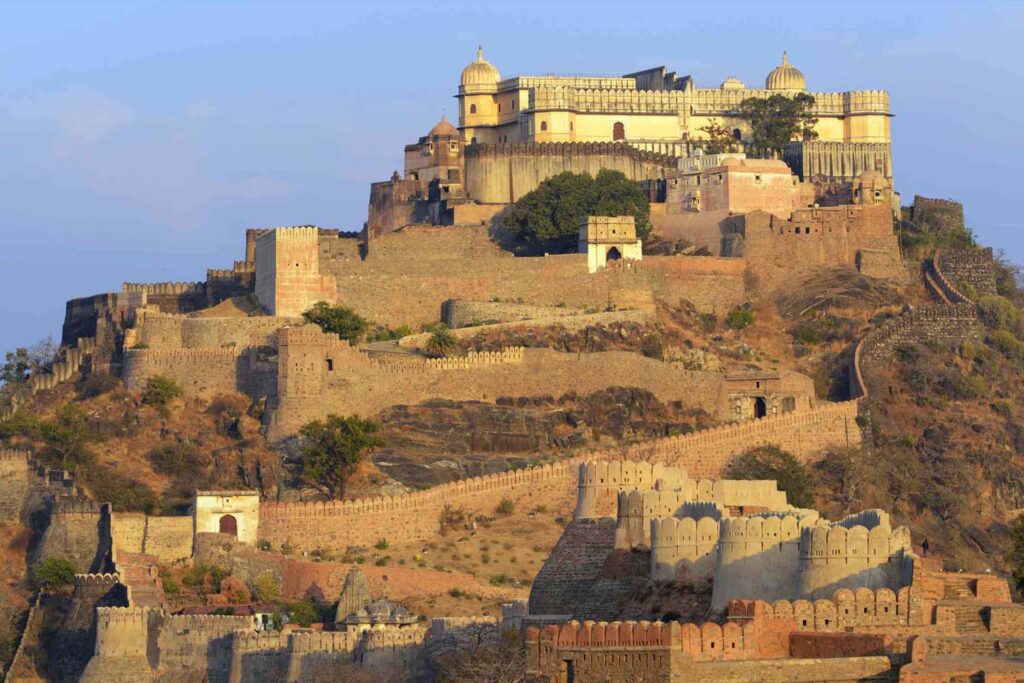
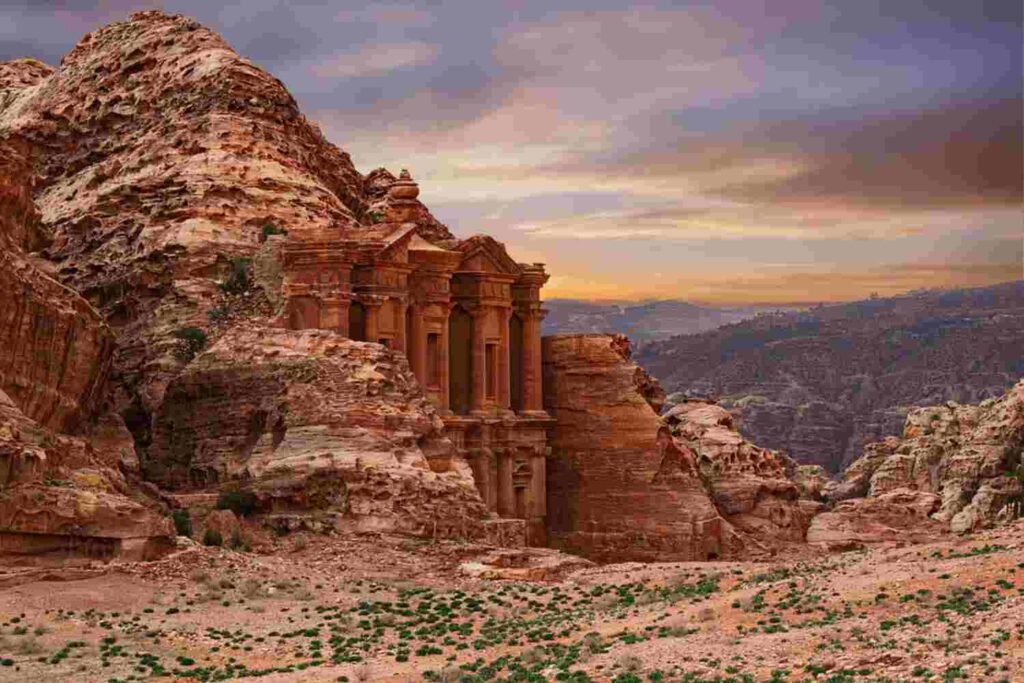
The world’s built heritage is rapidly disappearing due to factors such as natural disasters, neglect, urbanization, and armed conflict, according to a new report by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). The report reveals that “around 12% of the world’s cultural heritage sites have been damaged or destroyed in the past two decades alone, while many others remain at risk” (UNESCO, 2022).
One of the most significant threats to built heritage is armed conflict. In Syria, the ancient city of Aleppo has been heavily damaged by the country’s civil war, with many of its historic buildings and monuments destroyed or damaged beyond repair. In Afghanistan, the Taliban’s recent takeover of the country has raised concerns for the preservation of the country’s cultural heritage, including the Bamiyan Buddhas, two monumental statues that were destroyed by the Taliban in 2001 (UNESCO, 2022).
Urbanization and development are also major threats to built heritage. In China, the historic city of Shanghai has seen a rapid transformation in recent years, with many traditional neighborhoods and buildings demolished to make way for modern development. In India, the historic city of Ahmedabad has also seen significant changes due to urbanization, with many traditional buildings replaced by modern structures (UNESCO, 2022).
Basho valley Pakistan: Discover the unmatched beauty
Neglect and lack of maintenance are also contributing factors to the loss of built heritage. In Venice, Italy, the city’s historic buildings and canals are threatened by rising sea levels and neglect, with many buildings in need of restoration and preservation. In the United States, many historic buildings and sites are at risk due to lack of funding and maintenance, including the historic Alamo in San Antonio, Texas (National Trust for Historic Preservation, 2022).
Experts warn that the loss of cultural heritage has significant social and economic impacts, including the loss of cultural identity, community cohesion, and tourism revenue. According to a report by the International Council on Monuments and Sites, “cultural heritage sites generate significant economic benefits, including job creation and revenue from tourism, which can help support local economies and communities” (ICOMOS, 2021).
In conclusion, the rapid loss of cultural heritage around the world is a pressing issue that requires urgent attention and action. By raising awareness and investing in preservation and restoration efforts, we can help ensure that future generations can enjoy and learn from the world’s rich built heritage.
Statistics:
- Around 12% of the world’s cultural heritage sites have been damaged or destroyed in the past two decades alone (UNESCO, 2022)
- In Syria, the ancient city of Aleppo has been heavily damaged by the country’s civil war (UNESCO, 2022)
- In Afghanistan, the Bamiyan Buddhas were destroyed by the Taliban in 2001 (UNESCO, 2022)
- In China, the historic city of Shanghai has seen a rapid transformation in recent years (UNESCO, 2022)
- In India, the historic city of Ahmedabad has also seen significant changes due to urbanization (UNESCO, 2022)
- The Alamo in San Antonio,
- In Venice, Italy, many historic buildings and canals are threatened by rising sea levels and neglect (UNESCO, 2022)
- Around 30% of the world’s cultural heritage sites are located in conflict-affected areas (UNESCO, 2022)
- The loss of cultural heritage has significant social and economic impacts, including the loss of cultural identity, community cohesion, and tourism revenue (ICOMOS, 2021)
- Cultural heritage sites generate significant economic benefits, including job creation and revenue from tourism (ICOMOS, 2021)
 English
English